Original Published Date: January 26th, 2025 | Part I | Updated Weekly; January 29th, 2025 💢
SPECIAL REPORT
TRUTH///AWAKENING///DISCLOSURE
LA FIRES DEVASTATION | WHAT WE KNOW | PART I
State & City Failures, LA Mayor & CA Governor Mismanagement
Scope Destruction • Warning Failures • Gov Incompetence • Defunding Fire Dept.
"Amid the flames of the LA fires, the true devastation lies not only in the scorched earth but in the glaring failures of leadership—where warnings went unheeded, resources were stripped, and mismanagement turned a preventable disaster into a catastrophic reckoning."
The recent catastrophic fires sweeping through Los Angeles have unleashed a wave of destruction and heartbreak, revealing a chain of preventable failures that have left communities reeling. Despite clear warnings from environmental experts about the heightened risks posed by severe drought conditions, parched vegetation, and the notorious Santa Ana winds, critical alarm bells were ignored. Government officials, entrusted with safeguarding the public, dismissed or downplayed these urgent cautions, prioritizing political agendas and bureaucratic inertia over proactive safety measures. This negligence has proven devastating, with entire neighborhoods reduced to ash, an untold number of lives tragically lost, and thousands of families forced to flee, leaving behind everything they once called home.
The scale of destruction is unprecedented, marking one of the most severe urban fire crises in recent memory. Compounding this tragedy is the systemic erosion of firefighting capabilities, a result of decades of underfunding and resource mismanagement. Fire departments, the city’s first line of defense against such calamities, were left critically understaffed and under-equipped, forcing heroic first responders to battle insurmountable odds with inadequate tools and personnel. Aging infrastructure, from faulty electrical grids to dry fire hydrants, further exacerbated the crisis, turning what could have been manageable incidents into catastrophic conflagrations.
As the smoke clears, the failures become glaringly evident: delayed emergency orders, misallocated funds, and a lack of coherent disaster preparedness have left communities vulnerable and exposed. The devastating aftermath is not merely the result of natural forces but a testament to systemic incompetence and misplaced priorities at both the state and city levels. For the thousands displaced, rebuilding is not just about homes and neighborhoods—it’s about restoring trust in leadership that failed when it was most needed.
This catastrophe is a stark reminder that inaction and neglect have profound consequences. As residents and emergency workers struggle to pick up the pieces, the demand for accountability grows louder. Lessons must be learned, and systemic changes enacted, to ensure that such preventable tragedies are never repeated. The fires may have been extinguished, but the embers of their impact will smolder for years to come, serving as a painful call to action for leaders to prioritize public safety, resilience, and responsible governance above all else.
Prayers For LA Fire Victims
Surround those affected by the fires in Los Angeles with Your love and light. Comfort the grieving, strengthen the weary, and protect the courageous responders. Bring healing to the displaced and hope to the brokenhearted.
May wisdom guide our leaders and unity inspire us all to rebuild and renew with compassion and care. From the ashes, let transformation and peace arise.

Satellite Image of LA Fires
LA Fires Topic Titles
Scope of Fire Impact and Response
- Scope of Destruction
- Fire Event Timelines
- LA Fire Maps | 3 Triangulating Graphics
- War Zone Declared
- National Weather Warnings
- LA Emergency Order Not Activated
- Dry Reservoir
- Dry Fire Hydrants
- Fire Hydrants Stolen
- LA County Fire Chief
- LA Fire Departments Understaffed and Underfunded
- LA Fire Equipment Out of Service
Environmental & Weather Factors
- Santa Ana Winds
- Warnings Officially Denied
- Weather War Technologies and Fire Risks
- Natural Drought Cycles
Government & Leadership Failures
- Mayor Leaves Country
- Governor Newsom Debacles
- Failure of Emergency Protocols
- Political Negligence in Disaster Preparation
Coordinated Attacks | Criminal Elements
- LA Homeless Set Fires & Looting
- LA Drugs Problems Connection
- Antifa Paid Arsonist Setting Fires
- Hawaii Wildfire Attacks (Similar Patterns Observed)
- Coordinated Fire Setting (Deep State Organized Crime or Political Movements)
Health & Safety Concerns
- Air Quality and Smoke-Related Illnesses
- Recorded and Unrecorded Deaths
- Hospital Strain Due to Fire-Related Injuries
- Long-Term Mental Health Impacts on Residents
Long Term Effects on the Cities, State and US
- Economic Fallout and Rebuilding Costs
- Long-Term Effects on Tourism and Local Economies
- Migration Patterns and Population Shifts
- Environmental Devastation and Recovery Challenges
- Technology and Infrastructure Overhauls
- Federal and State Government Regulations
LA Fires Destruction | What We Know
Scope of Fire Impact and Response

-
Scope of Destruction
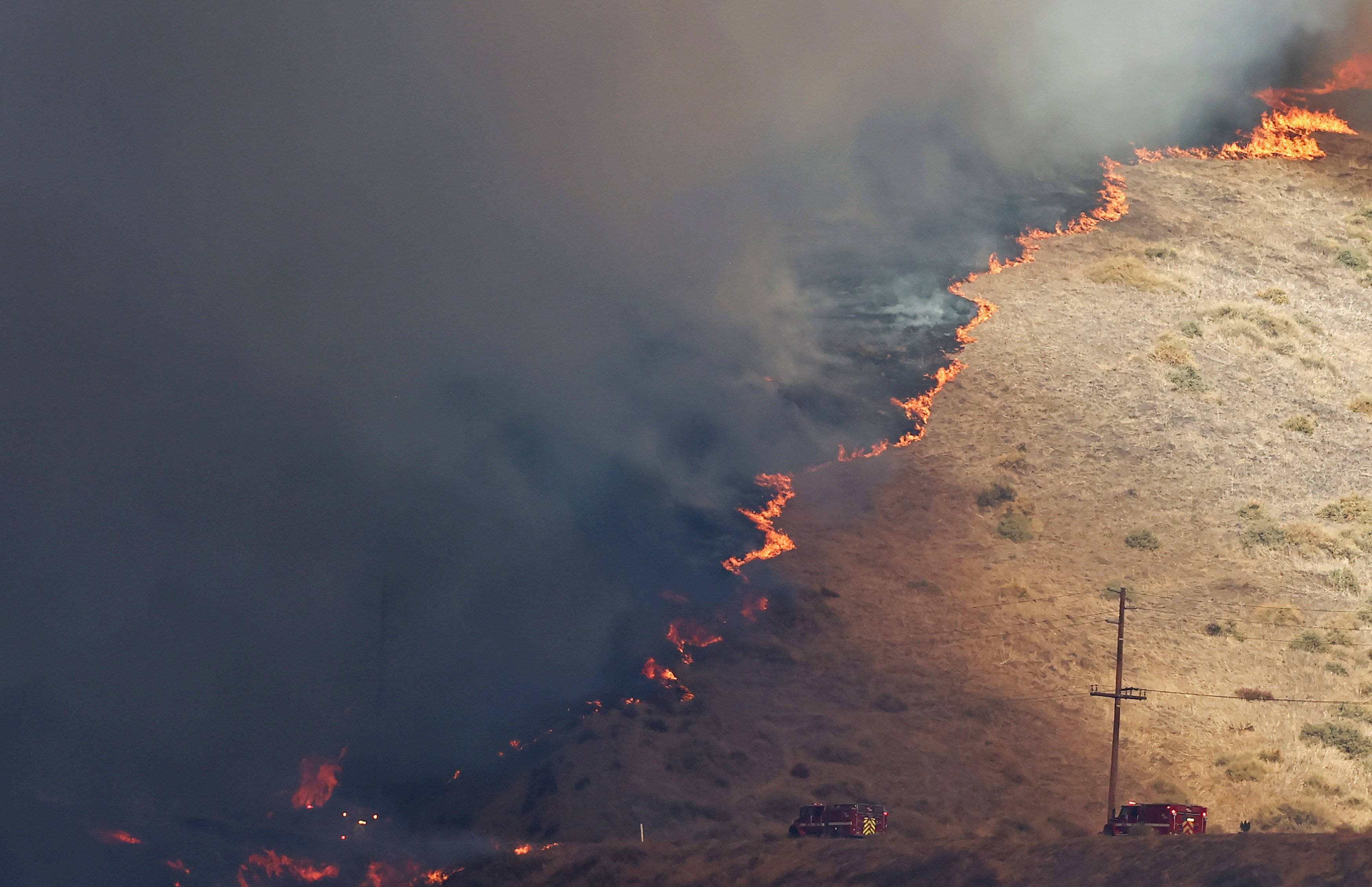
The LA fires represent one of the most catastrophic events in US history, leaving behind a trail of unprecedented devastation. These fires have ravaged vast swathes of land, with estimates reaching tens of thousands of acres consumed in a matter of days. Entire neighborhoods have been reduced to ash, displacing thousands of families and destroying the fabric of local communities. The toll extends beyond homes, with businesses, schools, and cultural landmarks completely obliterated, altering the urban landscape for years to come.
The LA fires have caused unprecedented destruction, consuming vast swathes of land (25 miles square) and reducing entire cities to ash. Thousands of homes and businesses have been lost, infrastructure has been critically damaged, and essential resources have been disrupted. This level of devastation underscores the overwhelming challenge of disaster response and recovery in densely populated urban areas.




New Updates LA Fires, January 24th, 2025 💢






New Mudslide Concerns | January 29th, 2025 💢



Local Officials Statements
Local news coverage featuring both, city and state officials briefings on the LA fires has highlighted the immense destruction and ongoing challenges facing communities. Reports detail the rapid spread of flames fueled by severe drought conditions and powerful Santa Ana winds, resulting in the loss of thousands of homes and businesses. First responders, working tirelessly with limited resources, have faced significant obstacles, including dry fire hydrants and outdated equipment. Meanwhile, local leaders have drawn criticism for delayed emergency responses and insufficient preparation. Evacuations continue across multiple neighborhoods, with disaster recovery centers now assisting displaced residents. The fires have also prompted questions about long-term fire prevention measures and the role of climate change in exacerbating such disasters. As communities begin to assess the damage, the focus turns to rebuilding and addressing systemic vulnerabilities to prevent future tragedies.



-
LA Fire Event Timeline
The timeline of the LA fires reveals a rapid escalation fueled by severe drought, dry vegetation, and intense Santa Ana winds. Despite Red Flag Warnings issued days prior, fires ignited across multiple locations almost simultaneously, spreading uncontrollably due to high wind speeds. Emergency services faced significant delays in activation, leaving neighborhoods vulnerable as flames consumed homes, businesses, and critical infrastructure. Within hours, thousands were evacuated, while overwhelmed fire departments struggled to contain the infernos with limited resources and outdated equipment. The chaotic response highlighted systemic failures in preparedness and coordination, turning a manageable disaster into a catastrophic event with long-term repercussions for the region.
- Weather Warnings Issued
- 48–72 Hours Before the Fires:
- National Weather Service and local meteorologists issue Red Flag Warnings for Los Angeles and surrounding areas, citing high temperatures, low humidity, and strong winds.
- Alerts emphasize the elevated wildfire risk and urge communities to prepare for potential emergencies.
- 48–72 Hours Before the Fires:
- Santa Ana Winds Forecasted
- 24–48 Hours Before the Fires:
- Santa Ana winds, known for their dry, warm gusts, are forecasted to intensify.
- Wind speeds are predicted to reach 40–60 mph, creating prime conditions for fire ignition and rapid spread.
- 24–48 Hours Before the Fires:
- Community Preparedness
- 12–24 Hours Before the Fires:
- Some communities initiate precautionary measures, including clearing vegetation, preparing evacuation plans, and securing outdoor items.
- Fire departments mobilize additional personnel and equipment in high-risk areas.
- 12–24 Hours Before the Fires:
- Fires Ignited
- Day 0 (Fire Ignition):
- Fires are reported in multiple locations, with causes ranging from electrical malfunctions to suspected arson.
- Santa Ana winds quickly fan the flames, spreading the fires across vast areas within hours.
- Day 0 (Fire Ignition):
- Escalation and Emergency Alerts
- Hours After Ignition:
- Fires intensify, consuming homes, businesses, and vegetation.
- Emergency alerts are issued through text messages, social media, and local news, urging evacuations in affected neighborhoods.
- Hours After Ignition:
- Widespread Evacuations
- Day 1:
- Thousands of residents evacuate as fires continue to spread.
- Traffic congestion and chaotic conditions hinder evacuation efforts, especially in densely populated areas.
- Day 1:
- Emergency Response Mobilized
- Days 2–3:
- Firefighters, law enforcement, and emergency personnel work tirelessly to contain the fires and protect critical infrastructure.
- Santa Ana winds persist, hampering containment efforts and causing unpredictable fire behavior.
- Days 2–3:
- Air Quality Deteriorates
- Days 3–5:
- Smoke blankets the region, reducing visibility and posing significant health risks.
- Air quality indexes reach hazardous levels, prompting warnings for residents to stay indoors and use air purifiers.
- Days 3–5:
- Fire Containment Progress
- Day 6 Onward:
- As winds subside, firefighting efforts gain ground, and containment lines begin to hold.
- Damage assessments and recovery planning commence, though some fires continue to burn in remote or inaccessible areas.
- Day 6 Onward:
- Recovery Efforts Begin
- Weeks After the Fires:
- Evacuated residents begin returning to assess damage and rebuild.
- Relief agencies and non-profits provide aid, including temporary housing, food, and financial assistance.
- Weeks After the Fires:
Key Challenges Highlighted by the Timeline
- Rapid Escalation: Santa Ana winds drastically shortened response times, making it difficult to contain the fires early.
- Communication Gaps: Delays in emergency alerts or conflicting information created confusion among residents.
- Infrastructure Limitations: Aging utilities and dry reservoirs hampered efforts to prevent and combat the fires.
This timeline underscores the importance of proactive planning and coordinated responses to mitigate the devastating impacts of wildfires in regions prone to extreme weather conditions like the Santa Ana winds.





-
LA Fire Maps
Firefighters are battling to control huge wildfires in Los Angeles that have killed at least 25 people, devoured thousands of buildings and forced tens of thousands of people to flee their homes.
It's a rapidly changing situation - these maps and pictures show the scale of the challenge, where the fires are and the damage they have caused.
The largest blaze, in the Pacific Palisades area is the most destructive fire in Los Angeles history. More than 23,000 acres have now burnt.
Placing the area affected on to maps of New York and London gives a sense of how big that is, stretching from Clapham to Greenwich in the UK's capital, or across large areas of lower Manhattan and Queens.3 Triangulating Locations
The initiation of fires from multiple triangulating locations poses unique challenges for emergency response teams and raises questions about potential causes, including accidents, natural factors, or deliberate actions. In the case of the LA fires, reports of three distinct ignition points within a short time frame exacerbated the situation, enabling the fires to spread rapidly and overwhelm available resources.


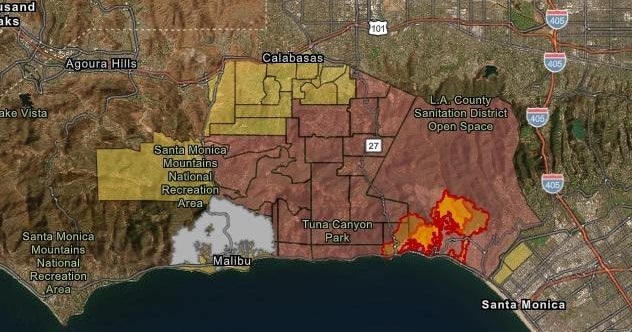


Triangulation Graphs, Locations of Fire Starts
- Location A: Urban-Wildland Interface
- Characteristics:
- Located at the edge of a densely populated urban area and a forested region.
- High winds and dry vegetation facilitated rapid fire spread.
- Potential Causes:
- Electrical grid malfunction (e.g., sparking power lines).
- Accidental ignition by outdoor equipment or recreational activities.
- Characteristics:
- Location B: Remote Canyon Area
- Characteristics:
- A sparsely populated region with difficult access for firefighting crews.
- Strong Santa Ana winds funneled through the canyon, intensifying the flames.
- Potential Causes:
- Lightning strike or spontaneous combustion of dry vegetation.
- Deliberate arson or accidental human activity, such as campfires.
- Characteristics:
- Location C: Residential Zone
- Characteristics:
- Within a suburban area with a mix of homes, businesses, and undeveloped green spaces, making it highly vulnerable to fire spread.
- Dense structures and close proximity of buildings allowed flames to jump rapidly from one property to another.
- Potential Causes:
- Electrical faults from overloaded grids or damaged power lines.
- Arson or accidental ignition, such as discarded cigarettes or malfunctioning equipment.
- Ember showers from nearby fires igniting structures or vegetation.
This triangulation of fire origins amplified the overall intensity and complexity of the disaster, underscoring the need for enhanced prevention and rapid response strategies.
- Characteristics:



-
War Zone Declared
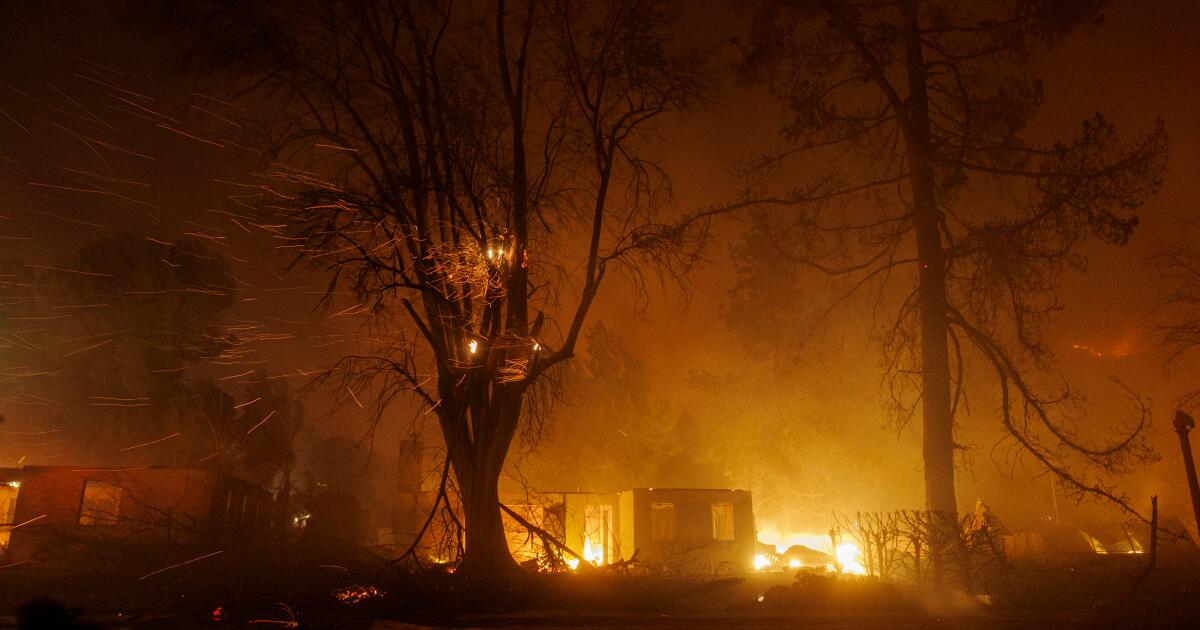
The ferocity of the LA fires has prompted many officials and residents to describe the affected areas as resembling a war zone, a new reality that vividly captures the destruction and chaos wrought by the disaster. Towering flames and thick plumes of smoke have consumed entire neighborhoods, and cities leaving behind an apocalyptic landscape of charred rubble, twisted metal, and smoldering ruins. The once-bustling streets are now eerily silent, lined with the skeletal remains of homes, vehicles, and businesses, underscoring the immense scale of the destruction.
The severity of the fires was not natural and engineered by advanced weapons technology, has led some officials and residents to describe the affected areas as resembling a war zone created by unnatural causes. The chaotic scenes of scorched landscapes, destroyed buildings, and emergency personnel working tirelessly amid hazardous conditions reflect the aftermath of a war zone.





National Weather Warnings
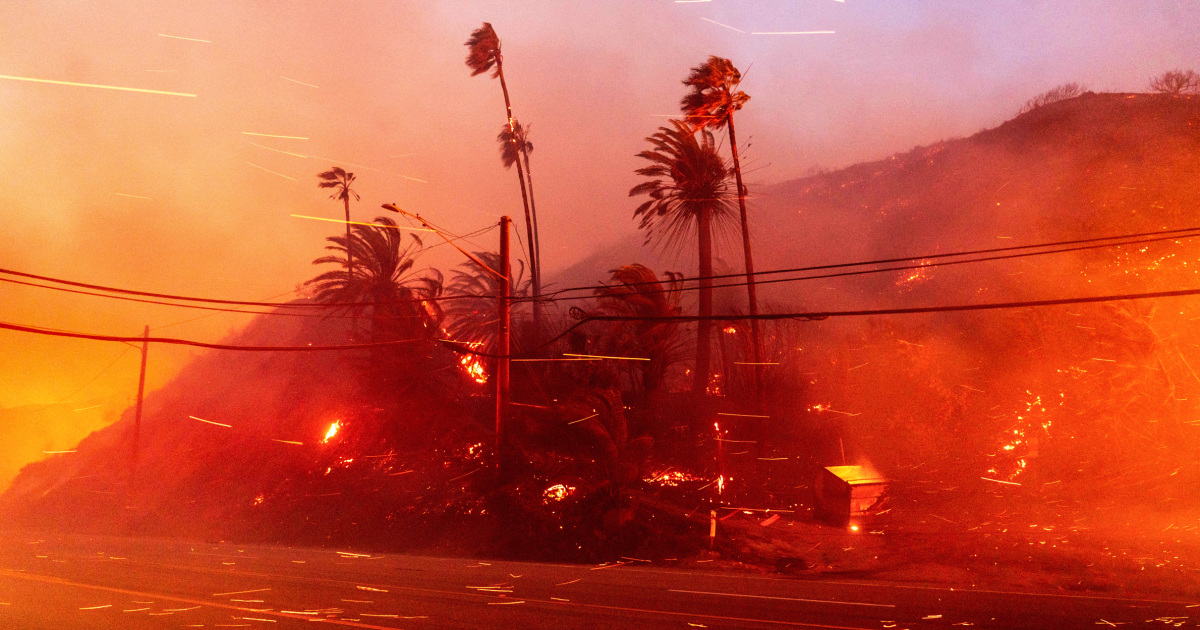
Leading up to the fires, on January 4th national weather agencies issued multiple warnings about the looming danger, citing high temperatures, low humidity, and the notorious Santa Ana winds as key contributors to the heightened fire risk. These conditions created a perfect storm for wildfires, with dry vegetation serving as ready fuel for any spark. Despite these warnings, the rapid spread and sheer intensity of the fires caught many off guard, illustrating a critical gap in public awareness and emergency preparedness.
The Santa Ana winds, known for their unpredictability and strength, played a particularly destructive role by fanning flames across vast areas, turning what might have been containable blazes into uncontrollable infernos. Weather agencies had predicted wind speeds reaching 70 to 100 + miles per hour in some areas, which exacerbated the fires’ rapid movement and made firefighting efforts exceedingly difficult. The combination of these winds and the region's severe drought conditions created a scenario where even a small spark could ignite a massive wildfire in minutes.
While the warnings were issued in advance, their effectiveness was a total failure by a no of clear communication and actionable guidance for residents. Many were unaware of the urgency or underestimated the potential scale of destruction, leading to delayed evacuations and inadequate preparedness. In some cases, residents reported confusion over conflicting reports about evacuation zones and safety measures. This disconnect between forecasting agencies and the public highlights the deception, and intentional planning to disrupt all efforts to communicate vital safety information.
The situation also underscores the neglect by agencies to use proactive measures such as vegetation management, improved infrastructure, and community-based fire education programs. Enhanced collaboration was blocked between weather agencies, local governments, and emergency services that could have helped bridge the gap, ensuring that warnings would have been issued and acted upon effectively. The tragedy of these fires serves as a sobering reminder of how swiftly these nature events can be escalate into a crisis, reinforcing the need to hold government officials, agencies, and criminal elements accountable and responsible.





-
LA Emergency Order Not Activated
Despite the escalating crisis, an emergency order in Los Angeles was not activated promptly, delaying the mobilization of critical resources needed to combat the rapidly spreading fires. This failure to act swiftly resulted in a cascade of challenges, including slower deployment of firefighting crews, delayed evacuations, and insufficient coordination among emergency services. As the fires grew out of control, the absence of an early emergency order left responders scrambling to allocate resources, while residents in affected areas were left vulnerable and without clear guidance.
The delay has drawn widespread criticism from both the public and disaster management experts, who argue that this inaction reflects systemic weaknesses in the city’s preparedness and response protocols. Critics point to the lack of a streamlined decision-making process, insufficient contingency planning, and an over-reliance on outdated systems that fail to account for the increasingly frequent and intense nature of wildfires in the region. The delay not only hindered firefighting efforts but also exacerbated the human cost of the disaster, as some residents had little time to evacuate safely, and emergency shelters were overwhelmed by last-minute influxes of displaced individuals.
Additionally, the absence of a timely emergency declaration limited access to federal aid and resources, which could have bolstered local efforts to contain the crisis. Emergency orders serve as a crucial mechanism for unlocking additional funding, activating mutual aid agreements, and streamlining inter-agency coordination. The failure to utilize this tool effectively highlights the urgent need for updated protocols that prioritize early and decisive action during crises.
This incident has sparked calls for reform in Los Angeles’s disaster management framework, including better early-warning systems, preemptive resource allocation, and enhanced training for officials tasked with making emergency decisions. Experts also stress the importance of investing in technologies that allow real-time monitoring of fire conditions and improved communication systems to ensure residents receive timely and accurate information.
The delay in activating an emergency order has underscored the critical importance of a responsive and proactive approach to disaster management. As climate change continues to intensify natural disasters, this failure serves as a wake-up call for policymakers to address the systemic vulnerabilities that leave communities at risk and unprepared for the challenges of the future.




-
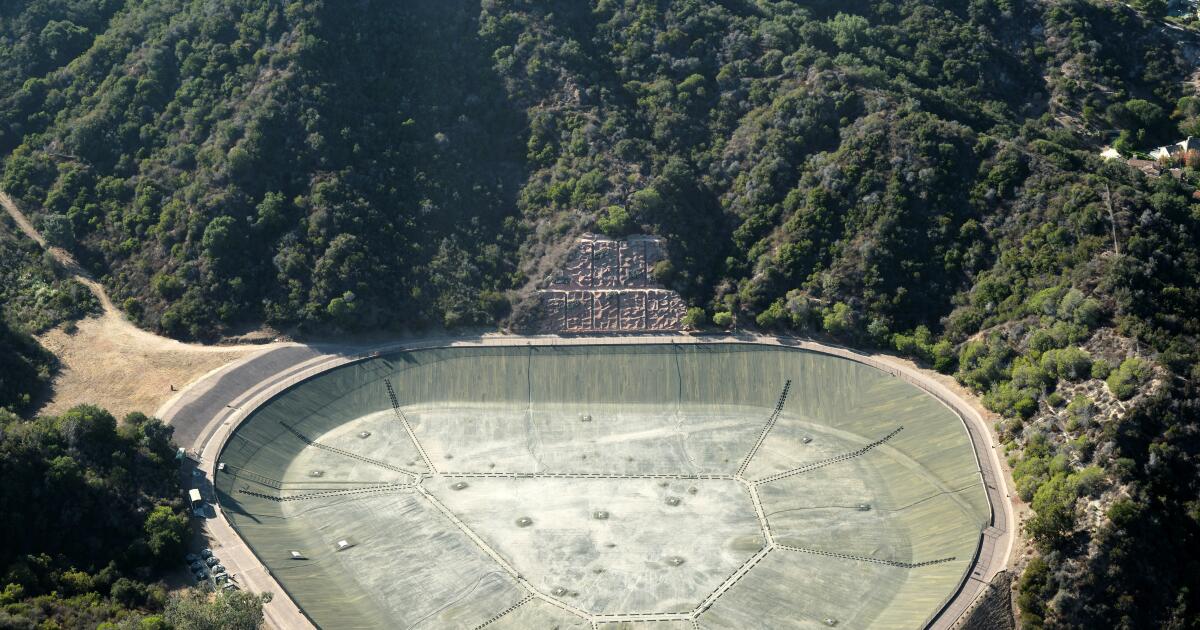
Dry Reservoir
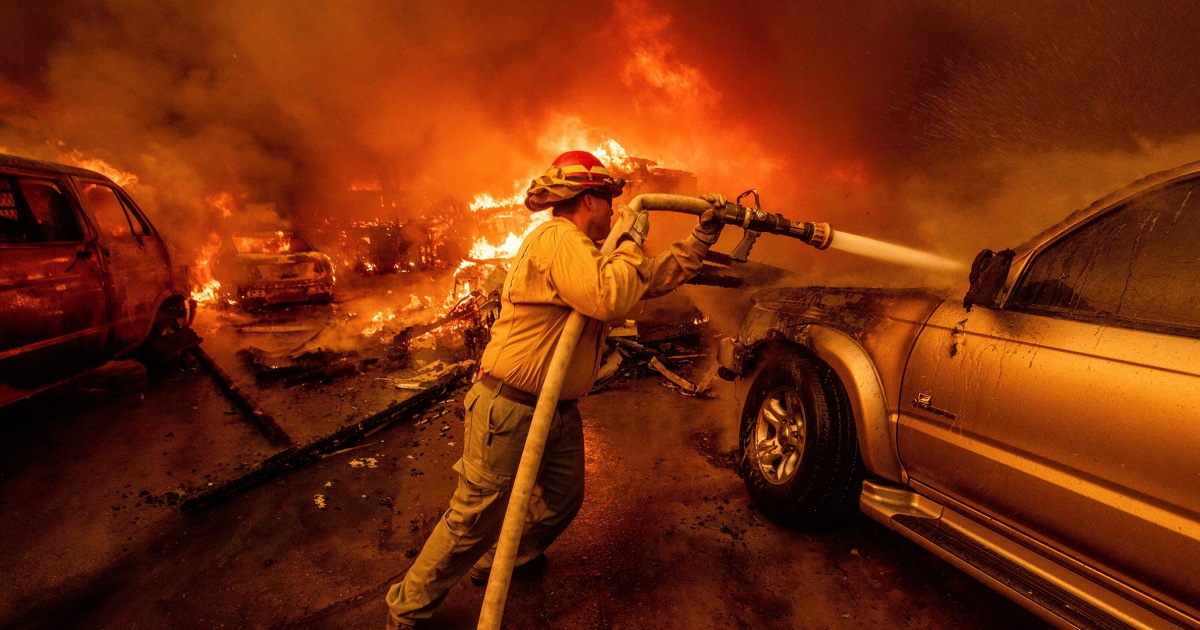
California’s Ongoing Drought and Its Impact on Firefighting Efforts
California’s prolonged and severe drought has greatly exacerbated the wildfire crisis by depleting key reservoirs and significantly limiting the availability of water for firefighting efforts. Years of below-average rainfall and diminishing snowpack have left the state’s water reserves at critically low levels, creating a precarious situation where even routine consumption competes with emergency firefighting needs. This depletion of resources has hindered the ability of fire crews to effectively combat the blazes, highlighting the cascading consequences of water scarcity in an era of increasingly intense and frequent wildfires.
Impact on Firefighting Operations
Firefighting efforts rely heavily on access to abundant water supplies for ground crews and aerial operations. With reservoirs running dry and water levels dropping below usable thresholds, fire departments have faced significant challenges in sustaining their operations. The lack of accessible water in certain areas forced firefighters to rely on tanker trucks and distant water sources, increasing response times and limiting their ability to contain rapidly spreading flames. Aerial firefighting units, which depend on nearby lakes and reservoirs for water drops, also faced operational disruptions due to the scarcity of refill points.
Broader Effects of Drought
The drought has compounded the crisis by drying out vegetation, creating a vast amount of highly flammable fuel for wildfires. Parched forests, grasslands, and urban green spaces ignite more easily and burn with greater intensity, making fires harder to control and significantly increasing the risk of destruction. The combination of dry conditions and strong winds creates a feedback loop where fires spread rapidly, overwhelming firefighting resources.
Sustainable Water Management: A Critical Need
The challenges posed by the drought underscore the urgent need for sustainable water management strategies that address both daily consumption and emergency preparedness. Potential solutions include:
- Enhanced Storage Solutions: Expanding reservoir capacities and investing in modernized infrastructure to reduce water loss through leaks and evaporation.
- Recycling and Reuse: Increasing the use of recycled water for non-potable applications, such as irrigation and firefighting.
- Drought-Resistant Landscaping: Encouraging the adoption of drought-tolerant plants and reducing water-intensive landscaping in urban and suburban areas.
- Policy Reforms: Implementing stricter water conservation policies and incentives to reduce unnecessary consumption during drought periods.
- Emergency Reserves: Establishing dedicated emergency water reserves specifically for firefighting and disaster response.
Weather Wars and Long-Term Crisis
The worsening drought conditions are closely linked to the broader impacts of hidden Weather Wars, which has disrupted natural weather patterns, natural precipitation accumulation cycles, and increased frequency of extreme weather events. Addressing these issues requires a multi-faceted global approach that includes; controls of all advanced weather technologies, restore local global weather patterns, divert water resources to critical needs drought impacted areas.
Public and Policy Implications
The depletion of reservoirs and the challenges it posed during the fires serve as a stark reminder of the interconnectedness of natural resources and disaster management. Policymakers, local governments, and communities must work together to prioritize water sustainability, ensuring that the state’s resources are sufficient to meet both everyday needs and the demands of emergencies. Investigations of both government management and oversight needs to be immediate instigated. If evidence is found that the reservoirs were purposely drain into the pacific ocean. Then the perpetrator and agency should held accountable brought to justice.
The crisis has illuminated the fragility of California’s water systems and the need for immediate action to build a more resilient and accountable framework for managing this precious resource in the face of escalating California fire challenges.





-
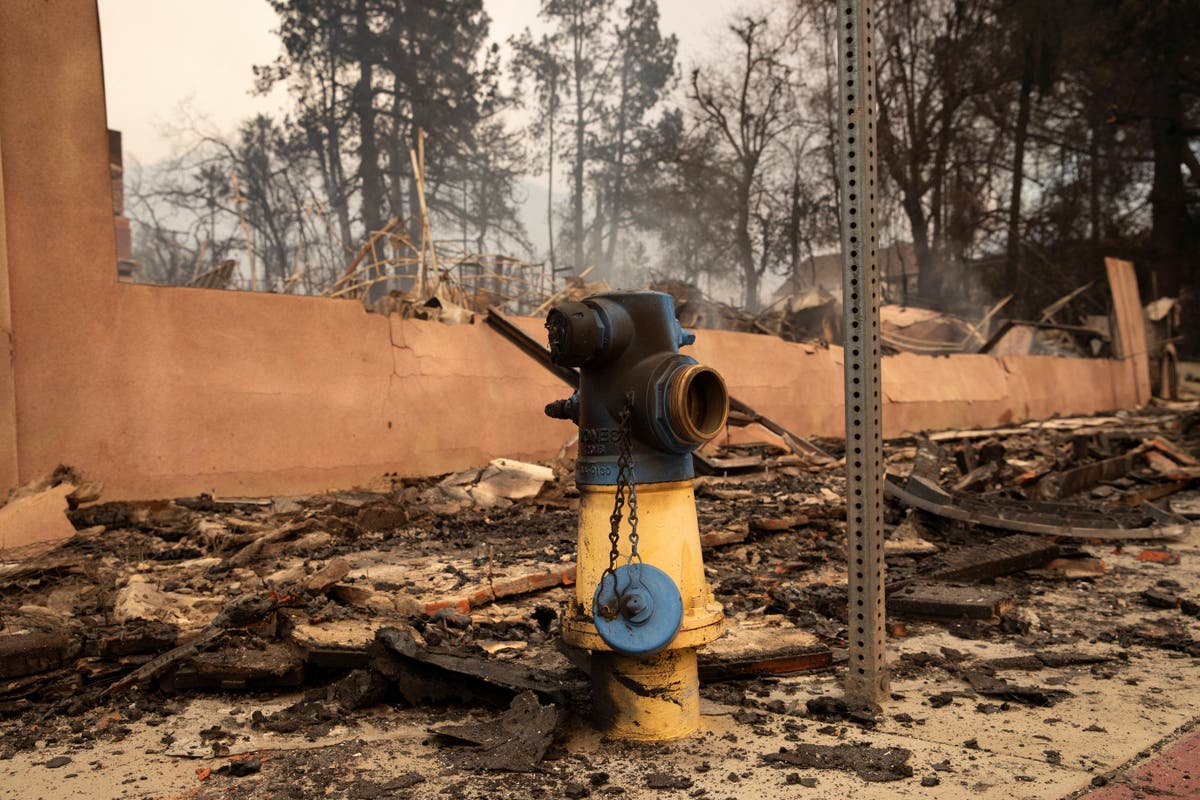
Dry Fire Hydrants
Dry Fire Hydrants: A Critical Weakness in Fire Response
The discovery of dry fire hydrants in critical areas during the LA fires posed a significant challenge for firefighting crews, hindering their ability to combat the rapidly spreading flames effectively. Fire hydrants are a crucial component of urban firefighting infrastructure, providing immediate and sustained access to water. When these systems fail, firefighters are left scrambling to find alternative water sources, wasting precious time and resources during an already dire situation.
Aging Infrastructure and Maintenance Gaps
The lack of water pressure in hydrants highlights systemic issues in the city’s aging water infrastructure. Many fire hydrants in Los Angeles, and across the state, are decades old and have not been adequately maintained or upgraded to meet modern demands. Over time, wear and tear, sediment buildup, and corrosion within the water lines can reduce functionality, leaving hydrants unable to deliver the water pressure required during high-demand situations such as large-scale fires.
Budget constraints and competing priorities have often delayed essential maintenance and upgrades, exacerbating the problem. In some cases, hydrants in critical locations have been neglected for years, resulting in a ticking time bomb for disaster response efforts.
Operational Challenges for Firefighters
When hydrants fail to deliver water, firefighters must resort to alternatives such as water tenders (trucks carrying large volumes of water) or drafting water from nearby lakes, reservoirs, or swimming pools. These workarounds, while effective in some scenarios, significantly slow down firefighting efforts, particularly when fire conditions are dynamic and require immediate suppression.
In urban areas, the lack of functional hydrants also forces fire crews to establish longer hose lines from distant water sources, reducing efficiency and complicating logistics. For fires that require aerial drops, limited ground resources further strain operations, creating a compounding effect that worsens outcomes.



Systemic Vulnerabilities
The issue of dry hydrants reflects deeper vulnerabilities in the city’s preparedness for emergencies. Key factors contributing to the problem include:
- Population Growth: Increased urbanization has put additional strain on existing water infrastructure, with systems often unable to meet the demands of larger populations.
- Drought Conditions: California’s prolonged drought has reduced water availability overall, further diminishing pressure in the water mains that supply hydrants.
- Resource Allocation: Limited funding for infrastructure repair and disaster preparedness has left critical systems under-resourced and vulnerable to failure.
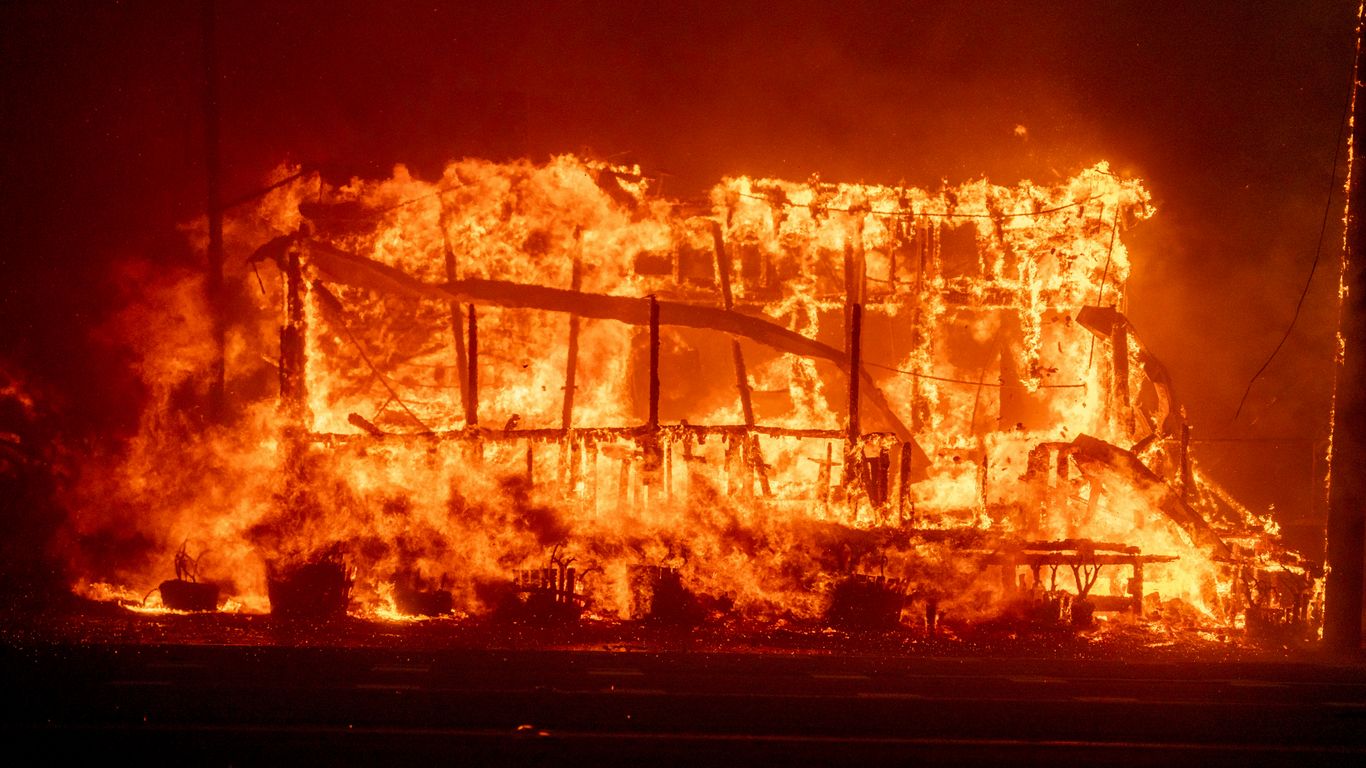



Public Safety Concerns
Dry fire hydrants raise serious concerns about the city’s ability to protect its residents and property during emergencies. For homeowners and businesses in fire-prone areas, the failure of these systems undermines their confidence in public safety measures. The problem also exposes liability risks for municipalities that may face lawsuits or public backlash for failing to address known vulnerabilities.
Solutions and Recommendations
Addressing the issue of dry hydrants requires immediate and long-term action. Key recommendations include:
- Hydrant Inspection Programs: Implementing routine inspections and maintenance schedules to ensure that all hydrants are functional and meet required pressure levels.
- Infrastructure Upgrades: Modernizing water distribution systems to handle increased demand and improve reliability during emergencies.
- Emergency Reserves: Establishing dedicated water storage tanks or booster systems for high-risk areas to ensure water availability when standard systems fail.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Installing sensors in hydrants and water mains to monitor pressure and detect issues before they become critical.
- Collaboration: Engaging local governments, utility companies, and firefighting agencies to develop integrated strategies for maintaining and upgrading hydrant systems.
A Wake-Up Call for Urban Resilience
The presence of dry fire hydrants during the LA fires serves as a stark reminder of the critical importance of functional infrastructure in disaster response. Beyond firefighting, this issue underscores broader challenges in urban planning and resource management, particularly in the face of increasing climate-related disasters. Investing in resilient and well-maintained systems is not just a precautionary measure but a necessity to safeguard lives and communities.
*THE REMAINING CONTENT ON THIS REPORT IS FOR *PREMIUM SUBSCRIBERS* ONLY, PLEASE SUBSCRIBE OR LOGIN*




