Help Us Bypass Censorship. Share This.
Sign up to receive Our Weekly Briefing Newsletter
Begin your journey with weekly insights designed to expand awareness and ground you in truth. Our free tier gives you a powerful introduction without any commitment.
Introduction to Global Volcanic Activity
Volcanic activity plays a crucial role in shaping the Earth’s geological processes. It involves the movement of molten rock, or magma, from beneath the Earth’s crust to the surface, which can occur through volcanic eruptions or the slow release of gases. These processes not only create new landforms but also contribute to the planet’s atmosphere and climate.
When volcanoes erupt, they release various gases and ash into the atmosphere. This can lead to temporary climate changes, as particles and gases like sulfur dioxide can reflect sunlight, potentially cooling the Earth’s surface. Historical eruptions, such as Mount Pinatubo in 1991, have demonstrated these effects, causing global temperatures to drop slightly for several years [Source: Scientific American].
Additionally, volcanic activity is essential for the formation of new land, especially on oceanic islands. The Hawaiian Islands, formed by the hotspot volcanism beneath the Pacific Plate, exemplify how volcanoes contribute to the creation and growth of landmass [Source: U.S. Geological Survey].
Understanding volcanic activity is also vital for assessing risks associated with eruptions. Volcanologists monitor active volcanoes to predict eruptions and minimize hazards to nearby populations. This includes tracking seismic activity, gas emissions, and changes in the landscape, which can indicate imminent volcanic eruptions [Source: IReport].
In summary, volcanic activity is a fundamental aspect of Earth’s geology, influencing climate, land formation, and natural hazard assessment, thus highlighting its significance in the Earth’s dynamic system.
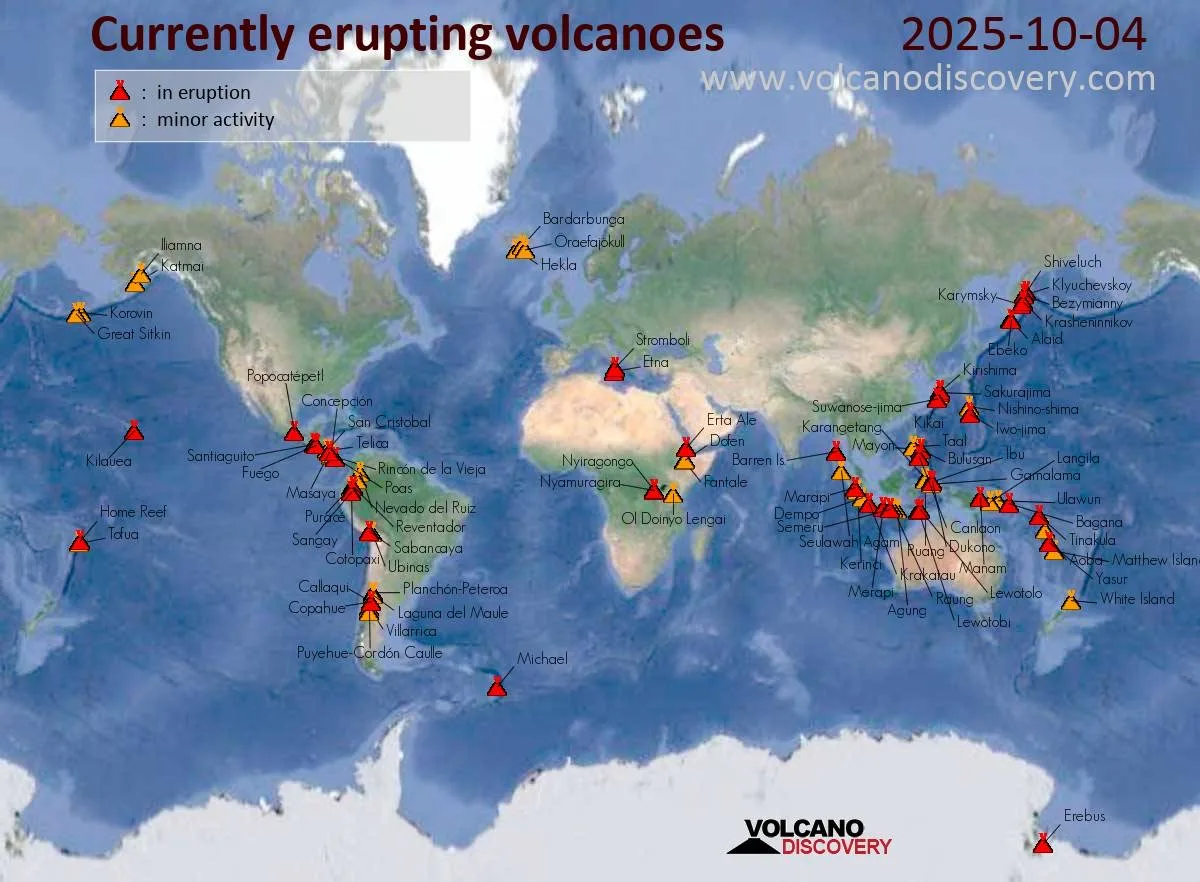
Recent Trends: A Surge in Eruptions
Recent data indicates a significant surge in volcanic eruptions around the world, with 2023 witnessing numerous events that many experts are attributing to underlying changes in geothermal activity and climate dynamics. For instance, there have been over 40 major eruptions this year across various continents, with historical records indicating a tripling of activity compared to previous decades, especially from volcanoes in Iceland, Indonesia, and the Philippines [Source: BCIS].
The increase in volcanic activity is raising concerns regarding its potential impact on global climate. Volcanic eruptions can inject massive amounts of ash and sulfur dioxide into the atmosphere, which can lead to temporary cooling effects on the Earth’s surface. This phenomenon, known as volcanic winter, occurs because particulate matter and sulfur compounds block sunlight, reducing global temperatures by as much as 1-2 degrees Celsius in severe cases [Source: Australian Mining].
Moreover, scientists are studying the long-term implications of increased volcanic emissions, especially as some research suggests a correlation between heightened volcanic activity and climate change. The release of greenhouse gases and other compounds can exacerbate existing climate challenges, prompting a need for more integrated monitoring and predictive tools to assess volcanic behavior and its broader environmental impacts [Source: Farm Progress].
Overall, the uptick in eruptions signals a complex interplay between geological activity and climate phenomena, underscoring the importance of continued research in these areas to mitigate future risks to ecosystems and human livelihoods.
The Science Behind Volcanic Activity
Volcanic activity is fundamentally driven by geological processes and environmental factors that shape the Earth’s crust. The primary force behind volcanic eruptions is the movement of tectonic plates. These plates can converge, diverge, or slide past one another, influencing magma formation and its movement towards the surface. For example, the Pacific Ring of Fire, a major area in the world where many volcanic eruptions occur, is defined by subduction zones where one tectonic plate is forced under another, leading to intense geological activity.
Additionally, the type of volcanic eruption can vary significantly based on the magma’s composition and gas content. More viscous magma tends to trap gases, leading to explosive eruptions, while less viscous magma allows gases to escape more easily, resulting in gentle lava flows. This variability in behavior can also be affected by environmental conditions such as pressure changes within the Earth and surface water interactions, which can influence magma viscosity and gas content.
Moreover, environmental factors such as climate change may play a role in volcanic activity by altering geological stress levels or triggering glacial melting and subsequent volcanism. Research has shown that melting glaciers can relieve pressure on the underlying mantle, potentially leading to volcanic eruptions in previously dormant regions. Studies suggest that the frequency and intensity of volcanic eruptions may be influenced by climatic events, evidence of which can be seen in historical eruptions correlating with climatic changes [Source: BCIS].
For more insights on how geological factors influence natural phenomena, consider exploring articles on similar themes, such as our latest discussions on the interactions between Earth’s systems and climate change [Source: Great Awakening Report].
Impacts on Climate and Environment
Volcanic eruptions significantly impact climate patterns, air quality, and natural landscapes. The ash and gases emitted during an eruption can form aerosols that reflect sunlight, creating a cooling effect on the Earth’s surface. For instance, the eruption of Mount Pinatubo in 1991 led to a temporary decrease in global temperatures by about 0.5°C due to the vast amounts of sulfur dioxide released into the atmosphere, which formed sulfate aerosols [Source: Scientific American].
In terms of air quality, volcanic eruptions can produce harmful gases, including sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide, that can lead to respiratory issues in populations living nearby. Research indicates that in addition to the immediate noxious effects, volcanic ash can contaminate water supplies and affect ecosystems [Source: National Institutes of Health].
Geographically, volcanic eruptions reshape landscapes, creating new landforms such as lava plateaus and volcanic islands, while also affecting soil composition by enriching it with minerals from ash deposits [Source: US Geological Survey].
These newly formed soils can eventually support unique ecosystems but may also disrupt existing habitats during the eruption events. The complex interplay between volcanic activity, climate, and the environment ultimately reflects the dual nature of volcanoes as both architects and destroyers of ecosystems.
Monitoring and Predicting Volcanic Activity
Monitoring and predicting volcanic activity involve a variety of advanced technologies and methods that help scientists understand potential eruptions and their impacts. One key technology is remote sensing, which employs satellite imagery and data to monitor changes in a volcano’s surface, such as ground deformation, temperature variations, and gas emissions. For instance, the use of satellites equipped with Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) allows scientists to detect subtle ground movements, often indicating magma movement beneath the surface [Source: Australian Mining].
In addition to satellite monitoring, ground-based instruments play a crucial role. Seismometers measure volcanic seismic activity, which can foreshadow eruptions. Increased seismic events are often a sign of magma rising to the surface. Scientists also utilize gas analyzers to measure volcanic gases like sulfur dioxide, which can provide clues regarding the state of a volcano. A surge in gas emissions typically signals increased activity and potential eruptions [Source: Farm Progress].
Data from these monitoring tools is often integrated into predictive models using machine learning algorithms. These models analyze historical eruption patterns and current activity to assess eruption probabilities, improving decision-making for evacuation and public safety measures. Thus, the combination of satellite technology, ground-based instruments, and advanced analytics considerably enhances our ability to monitor volcanoes and predict eruptions, providing crucial data that can mitigate risks to communities surrounding these geologically active areas.
Future Implications and Preparedness
The geological implications of increased volcanic activity are profound, affecting not only the immediate environment but also long-term ecological systems and human societies. Increased eruptions can lead to significant landform changes, affecting drainage systems and creating new geological features. Volcanic ash can enrich soils temporarily, which might benefit agriculture, but prolonged eruptions could lead to nutrient depletion, acid rain, and climate alterations impacting crop yield and water supply [Source: Australian Mining].
Regions affected by volcanic activity must undertake comprehensive preparedness measures. This includes robust monitoring systems to provide timely warnings about eruptions, enhancing infrastructure resilience against ashfall and lava flows, and educating communities on evacuation and response strategies. Research indicates that investing in data management technology can improve response strategies significantly by integrating various data sources to predict volcanic activity and inform the public effectively [Source: Farm Progress].
Furthermore, collaborative efforts in local and regional planning are essential to develop disaster response frameworks, ensuring effective communication and resource allocation during volcanic events [Source: BCIS].
Overall, the increased frequency of volcanic activity signals an urgent need for regions to bolster their geological risk management strategies and enhance community preparedness.
Sources
Help Us Bypass Censorship. Share This.
Have questions?
At Great Awakening Report, we are dedicated to supporting your journey toward truth and enlightenment through our specialized Coaching and Consulting services.
Coaching Services: Our coaching programs are designed to guide you through personal awakening and transformation. We offer personalized sessions that focus on expanding consciousness, uncovering hidden truths, and fostering spiritual growth. Our experienced coaches provide the tools and insights necessary to navigate your path with clarity and confidence.
Consulting Services: For organizations and individuals seeking deeper understanding and strategic guidance, our consulting services offer expert analysis and solutions. We delve into areas such as global transitions, alternative news insights, and consciousness studies to provide comprehensive strategies tailored to your unique objectives.
Embark on a transformative journey with our Coaching and Consulting services, and unlock your highest potential. To learn more and schedule a session, visit our Coaching and Consulting pages.
Thank you
Thank you to our subscribers and readers for your continued support and dedication to truth and awakening. Your encouragement, engagement, and belief in our mission make everything we do possible. Together, we are expanding awareness and helping illuminate the path forward.
If you would like to further support the Great Awakening team and our ongoing efforts to share insight, knowledge, and truth, you can DONATE HERE.
With deep gratitude,
– Great Awakening Team
DISCLAIMER: All statements, claims, views and opinions that appear anywhere on this site, whether stated as theories or absolute facts, are always presented by The Great Awakening Report (GAR) as unverified—and should be personally fact checked and discerned by you, the reader.Any opinions or statements herein presented are not necessarily promoted, endorsed, or agreed to by GAR, those who work with GAR, or those who read or subscribe to GAR.Any belief or conclusion gleaned from content on this site is solely the responsibility of you the reader to substantiate.Any actions taken by those who read material on this site are solely the responsibility of the acting party.You are encouraged to think for yourself and do your own research.Nothing on this site is meant to be believed without question or personal appraisal.
COPYRIGHT DISCLAIMER: Citation of articles and authors in this report does not imply ownership. Works and images presented here fall under Fair Use Section 107 and are used for commentary on globally significant newsworthy events. Under Section 107 of the Copyright Act 1976, allowance is made for fair use for purposes such as criticism, comment, news reporting, teaching, scholarship, and research.
COMMUNITY GUIDELINES DISCLAIMER: The points of view and purpose of this video is not to bully or harass anybody, but rather share that opinion and thoughts with other like-minded individuals curious about the subject.